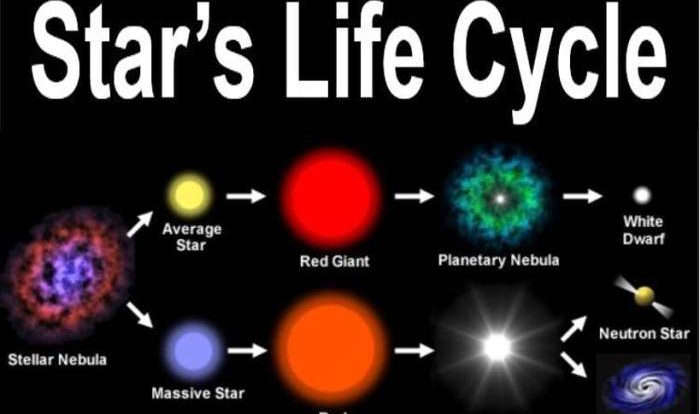
Delve into the enigmatic world of stars with the H-R diagram worksheet answer key, a celestial guide that illuminates the properties and characteristics of these cosmic beacons.
This comprehensive resource unravels the mysteries of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, a tool that classifies stars based on their luminosity and temperature, providing a deeper understanding of stellar evolution and the universe beyond.
1. Understanding the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram is a scatter plot that displays the relationship between the luminosity and surface temperature of stars. It is a fundamental tool in astronomy, as it allows astronomers to classify stars based on their physical properties.The horizontal axis of the H-R diagram represents the surface temperature of the star, which is measured in Kelvin.
The vertical axis represents the luminosity of the star, which is measured in solar luminosities (L☉). The Sun has a luminosity of 1 L☉.The H-R diagram is divided into several regions, each of which corresponds to a different type of star.
The main regions are:*
-*Main sequence
This is the diagonal band that runs from the upper left to the lower right of the diagram. Main sequence stars are stars that are fusing hydrogen in their cores.
-
-*Red giants
These are stars that have exhausted the hydrogen in their cores and are now fusing helium. They are located in the upper right of the diagram.
-*White dwarfs
These are stars that have exhausted all of their nuclear fuel and are now cooling down. They are located in the lower left of the diagram.
-*Supergiants
These are very large, luminous stars that are located in the upper left of the diagram.
-*Neutron stars
These are very small, dense stars that are formed from the collapsed cores of massive stars. They are located in the lower left of the diagram.
-*Black holes
These are regions of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. They are located in the lower left of the diagram.
The H-R diagram is a powerful tool that allows astronomers to understand the evolution of stars. By studying the position of a star on the H-R diagram, astronomers can determine its age, mass, and chemical composition.
2. Types of Stars on the H-R Diagram
The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram is a graphical representation of the relationship between the luminosity and temperature of stars. It reveals the diverse characteristics and evolutionary paths of different star types.
Main Sequence Stars
Main sequence stars, located along the diagonal band in the H-R diagram, represent the majority of stars in the universe. They are characterized by their stable fusion of hydrogen in their cores, which generates their energy and luminosity. The temperature and luminosity of main sequence stars vary depending on their mass, with more massive stars being hotter and more luminous.
Red Giants
Red giants, situated in the upper right region of the H-R diagram, are stars that have exhausted their hydrogen fuel in their cores and are now fusing heavier elements. As a result, they expand in size and become cooler, resulting in their reddish appearance.
Red giants are typically more luminous than main sequence stars but have lower surface temperatures.
White Dwarfs
White dwarfs, found in the lower left corner of the H-R diagram, are the final evolutionary stage for low-mass stars. They are compact, Earth-sized remnants of stars that have shed their outer layers and cooled significantly. White dwarfs are supported by electron degeneracy pressure and emit a faint, white glow due to their high surface temperatures.
Spectral Class, Luminosity, and Mass
The table below summarizes the characteristics of different star types based on their spectral class, luminosity, and mass:| Spectral Class | Luminosity | Mass ||—|—|—|| O, B | Supergiant, Giant, Main Sequence | 10
100 M☉ |
| A, F | Main Sequence | 1.5
10 M☉ |
| G, K | Main Sequence, Subgiant, Giant | 0.8
1.5 M☉ |
| M | Main Sequence, Red Dwarf | 0.08
0.8 M☉ |
3.
Interpreting the H-R Diagram
The H-R diagram is a powerful tool for astronomers to understand the properties of stars. By studying the position of a star on the diagram, astronomers can determine its age, mass, and luminosity.
The H-R diagram shows a clear relationship between a star’s position and its age. Younger stars are typically found on the main sequence, a diagonal band that runs from the upper left to the lower right of the diagram. As stars age, they move off the main sequence and become red giants or white dwarfs.
The H-R diagram also shows a relationship between a star’s position and its mass. More massive stars are found on the upper left of the diagram, while less massive stars are found on the lower right. The mass of a star determines its luminosity, or brightness.
More massive stars are more luminous than less massive stars.
Using the H-R Diagram to Study Stellar Evolution and Stellar Populations
Astronomers use the H-R diagram to study stellar evolution and stellar populations. By tracking the movement of stars on the diagram over time, astronomers can learn about the different stages of a star’s life. They can also use the diagram to study the distribution of stars in different galaxies and star clusters.
The H-R diagram is a valuable tool for astronomers to understand the properties of stars and the evolution of galaxies.
4. Applications of the H-R Diagram: H-r Diagram Worksheet Answer Key
The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram serves as a powerful tool for astronomers to unravel the mysteries of stars and galaxies. By mapping the relationship between stellar luminosity and temperature, the H-R diagram provides insights into the formation, evolution, and distribution of stars.
Understanding Stellar Formation and Clusters
The H-R diagram helps astronomers understand how stars form and evolve within stellar clusters. By studying the distribution of stars on the diagram, astronomers can determine the age and composition of clusters. For instance, young clusters contain numerous hot, luminous stars, while older clusters exhibit a larger proportion of cooler, less massive stars.
This information allows astronomers to trace the evolutionary history of stellar populations.
Tracing the Evolution of Galaxies
The H-R diagram also contributes to our understanding of galaxy evolution. By analyzing the H-R diagrams of different galaxies, astronomers can infer their star formation rates, metallicity, and overall evolutionary status. For example, galaxies with high star formation rates exhibit a large number of blue, luminous stars, while galaxies with low star formation rates have more red, cooler stars.
This information helps astronomers understand the factors that drive galaxy formation and evolution.
Notable Discoveries Enabled by the H-R Diagram, H-r diagram worksheet answer key
The H-R diagram has played a pivotal role in several astronomical discoveries. One notable example is the discovery of white dwarf stars. These faint, compact stars were initially puzzling until astronomers realized that they represented the final stage in the evolution of low-mass stars.
The H-R diagram also helped identify the existence of red giants, which are stars that have exhausted their nuclear fuel and expanded to enormous sizes. These discoveries have significantly advanced our understanding of stellar life cycles.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the H-R diagram?
The H-R diagram is a graph that plots the luminosity of stars against their surface temperature, providing insights into their properties and evolutionary paths.
How can I use the H-R diagram worksheet answer key?
The worksheet answer key provides guidance on interpreting the H-R diagram, enabling users to identify different types of stars and understand their characteristics.
What are the main types of stars on the H-R diagram?
The H-R diagram classifies stars into various types, including main sequence stars, red giants, white dwarfs, and supergiants, each with distinct properties and evolutionary trajectories.