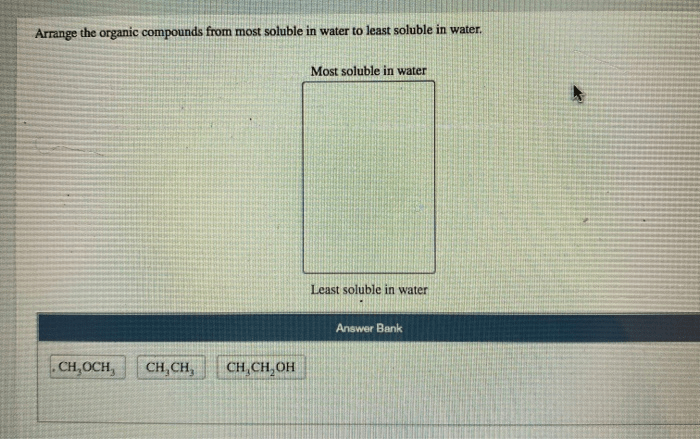
Arrange the organic compounds from most soluble in water – In the realm of chemistry, the solubility of organic compounds in water is a fundamental concept that governs their behavior and applications. This guide delves into the factors that influence water solubility, exploring the intricate relationship between molecular structure and solubility.
We will unravel the role of polarity, hydrogen bonding, and functional groups in determining the solubility of organic compounds. Additionally, we will examine the impact of molecular weight, branching, and chain length on their aqueous behavior.
Factors Affecting Water Solubility
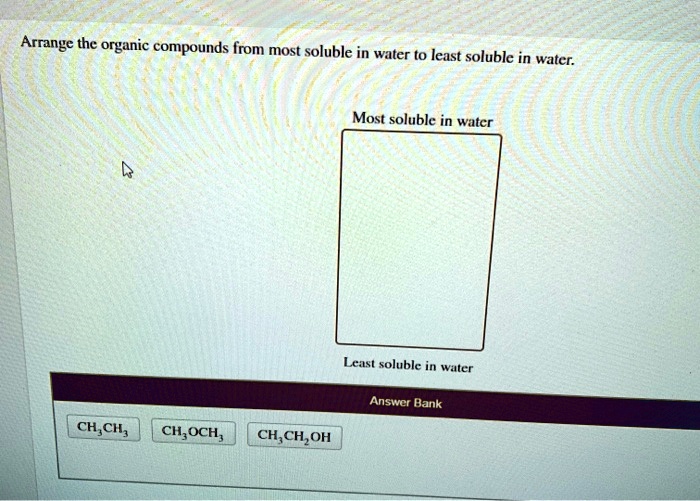
The solubility of organic compounds in water is influenced by various factors, including polarity, hydrogen bonding, and functional groups.
Polarity of Organic Compounds
Polarity refers to the uneven distribution of electrons within a molecule. Organic compounds with polar functional groups, such as alcohols and ketones, have a dipole moment and are more soluble in water than nonpolar compounds, such as hydrocarbons.
Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen bonding occurs between a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative atom (such as oxygen or nitrogen) and another electronegative atom. Water molecules form extensive hydrogen bonds with each other, and polar organic compounds can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, enhancing their solubility.
Functional Groups
The presence of certain functional groups can enhance or hinder water solubility. For example, hydroxyl (-OH) and carboxylic acid (-COOH) groups increase water solubility due to their ability to form hydrogen bonds. In contrast, alkyl groups (-CH3) decrease water solubility as they are nonpolar.
Structural Features and Water Solubility
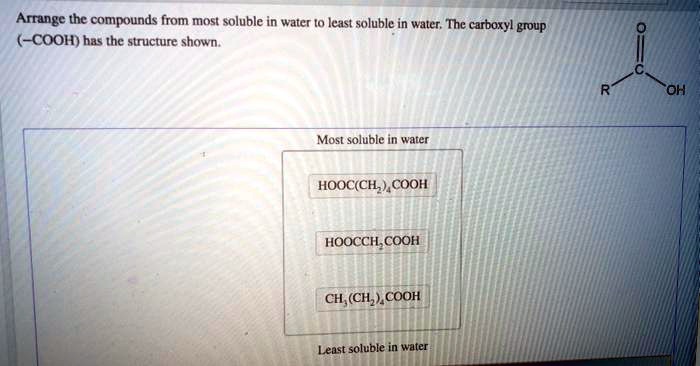
The structural features of organic compounds also influence their water solubility.
Molecular Weight
In general, as molecular weight increases, water solubility decreases. This is because larger molecules have a more difficult time forming hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
Branching and Chain Length, Arrange the organic compounds from most soluble in water
Branching and chain length can also affect water solubility. Branched molecules are generally less soluble in water than unbranched molecules because the branches disrupt the formation of hydrogen bonds. Similarly, longer chain molecules are less soluble than shorter chain molecules due to their increased nonpolar character.
Influence of pH and Temperature

The solubility of organic compounds in water can be affected by pH and temperature.
pH
The pH of the water can affect the solubility of organic acids and bases. For example, the solubility of organic acids increases as the pH decreases (becomes more acidic) because the protonation of the acid makes it more polar and able to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
Temperature
Temperature can also affect water solubility. In general, the solubility of organic compounds increases with increasing temperature. This is because the increased kinetic energy at higher temperatures helps to overcome the intermolecular forces between the organic compound and water molecules.
Experimental Determination of Water Solubility: Arrange The Organic Compounds From Most Soluble In Water
The water solubility of organic compounds can be experimentally determined using various methods.
Shake-Flask Method
The shake-flask method is a simple and widely used method for determining water solubility. In this method, an excess of the organic compound is added to a known volume of water and the mixture is shaken vigorously. After equilibrium is reached, the concentration of the organic compound in the water is determined using analytical techniques such as UV-Vis spectrophotometry or HPLC.
Helpful Answers
What is the most important factor affecting the water solubility of organic compounds?
Polarity is the most significant factor influencing water solubility. Polar compounds tend to be more soluble in water than nonpolar compounds.
How does hydrogen bonding affect water solubility?
Hydrogen bonding between organic compounds and water molecules enhances water solubility. Compounds with hydrogen bond donors or acceptors exhibit increased solubility.
What is the relationship between molecular weight and water solubility?
Generally, as molecular weight increases, water solubility decreases. Larger molecules have more difficulty penetrating the polar water environment.