The dna vs rna amoeba sisters answer key provides a captivating exploration into the fundamental differences between DNA and RNA, delving into their molecular structures, biological roles, and significance within the context of Amoeba Sisters’ educational videos.
This comprehensive guide unravels the complexities of these essential molecules, highlighting their unique characteristics and functions in cellular processes, making it an invaluable resource for students, educators, and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of molecular biology.
DNA vs. RNA Overview: Dna Vs Rna Amoeba Sisters Answer Key
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are two essential biomolecules that play crucial roles in the transmission, expression, and regulation of genetic information within living organisms. Both DNA and RNA are composed of nucleotide subunits, but they differ in their chemical structure, function, and location within the cell.
DNA is a double-stranded molecule that primarily serves as the genetic blueprint for an organism. It is found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and in the nucleoid region of prokaryotic cells. DNA contains the genetic code that determines the sequence of amino acids in proteins, the building blocks of life.
RNA is a single-stranded molecule that plays a diverse range of roles in cellular processes. It is involved in protein synthesis, gene regulation, and the transfer of genetic information. RNA is found in both the nucleus and cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells and in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells.
Key Differences between DNA and RNA
- Structure:DNA is a double-stranded molecule, while RNA is a single-stranded molecule.
- Sugar-Phosphate Backbone:DNA contains deoxyribose sugar, while RNA contains ribose sugar.
- Nitrogenous Bases:DNA contains the nitrogenous bases adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine, while RNA contains adenine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil.
- Location:DNA is primarily found in the nucleus, while RNA is found in both the nucleus and cytoplasm.
- Function:DNA stores genetic information, while RNA participates in protein synthesis, gene regulation, and other cellular processes.
Structural Analysis
DNA and RNA are two essential molecules in molecular biology that play vital roles in the transmission of genetic information. Understanding their structural differences is crucial for comprehending their distinct functions.
Composition and Organization
Both DNA and RNA are composed of nucleotide subunits. Each nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a sugar molecule, and a phosphate group. However, they differ in their specific components:
- DNAcontains the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Its sugar molecule is deoxyribose.
- RNAcontains the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), uracil (U), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Its sugar molecule is ribose.
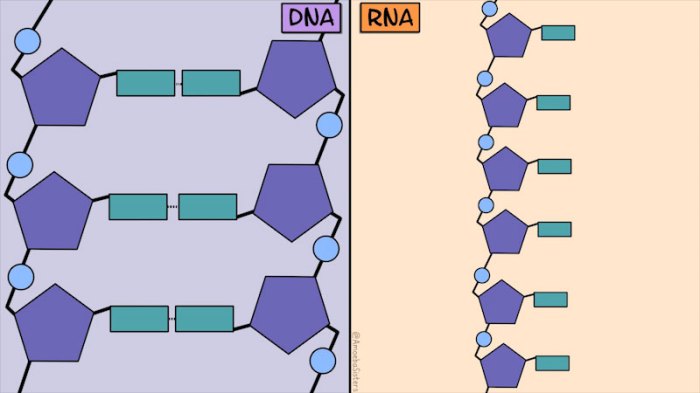
The organization of these nucleotides within the molecule also differs. DNA typically exists as a double helix, consisting of two antiparallel strands held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs (A-T and C-G). RNA, on the other hand, usually exists as a single-stranded molecule.
Structural Differences
The following diagram illustrates the key structural differences between DNA and RNA:
The diagram shows that DNA has a double helix structure with a backbone of alternating deoxyribose and phosphate groups. The nitrogenous bases project inward, forming hydrogen bonds between complementary pairs. RNA, on the other hand, has a single-stranded structure with a backbone of alternating ribose and phosphate groups.
The nitrogenous bases project outward, and there is no base pairing.
Biological Roles
DNA and RNA play crucial roles in cellular processes. DNA stores the genetic information necessary for the development and functioning of organisms, while RNA is involved in various aspects of protein synthesis and gene regulation.
DNA is a double-stranded molecule that contains the genetic code for an organism. It is found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the amino acid sequence of proteins, which are the building blocks of cells.
RNA is a single-stranded molecule that is involved in protein synthesis. There are several types of RNA, including messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). mRNA carries the genetic code from DNA to the ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized.
tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes in the correct order, as specified by the mRNA. rRNA is a component of the ribosomes and helps to catalyze the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids.
DNA as Genetic Material
DNA is the genetic material of all living organisms, except for some viruses. It is a double-stranded molecule that contains the instructions for an organism’s development and functioning. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the amino acid sequence of proteins, which are the building blocks of cells.
RNA in Protein Synthesis
RNA is involved in various aspects of protein synthesis. Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the genetic code from DNA to the ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized. Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings amino acids to the ribosomes in the correct order, as specified by the mRNA.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a component of the ribosomes and helps to catalyze the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids.
Comparison in Amoeba Sisters
The Amoeba Sisters’ educational videos play a pivotal role in understanding the significance of DNA and RNA. These videos effectively convey the differences between these molecules through engaging animations, clear explanations, and relatable examples.
DNA vs. RNA: Structural Differences
The videos highlight the structural differences between DNA and RNA, emphasizing the presence of deoxyribose sugar in DNA and ribose sugar in RNA. They also explain the double-stranded nature of DNA and the single-stranded nature of RNA, visually demonstrating how these structural variations contribute to their distinct functions.
DNA vs. RNA: Biological Roles, Dna vs rna amoeba sisters answer key
The Amoeba Sisters’ videos emphasize the biological roles of DNA and RNA. They explain that DNA serves as the genetic blueprint, storing hereditary information that is passed down from one generation to the next. RNA, on the other hand, is involved in protein synthesis, acting as a messenger molecule that carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes, where proteins are assembled.
Visual Aids and Examples
The videos incorporate visual aids and examples to make the concepts more accessible. They use animated diagrams to illustrate the structure of DNA and RNA, and provide real-life examples to demonstrate the importance of these molecules in biological processes.
Interactive Quizzes and Activities
To reinforce understanding, the Amoeba Sisters’ videos include interactive quizzes and activities. These interactive elements allow students to test their knowledge and engage with the material in a hands-on manner, enhancing their comprehension of the differences between DNA and RNA.
Illustrative Examples
To enhance understanding, let’s explore an infographic and real-world examples showcasing the distinct characteristics and applications of DNA and RNA.
Infographic on Key Differences
The infographic below visually depicts the fundamental differences between DNA and RNA:
- Sugar-Phosphate Backbone:DNA has deoxyribose sugar, while RNA has ribose sugar.
- Nitrogenous Bases:DNA contains adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine, while RNA replaces thymine with uracil.
- Double vs. Single Strand:DNA typically exists as a double helix, whereas RNA is generally single-stranded.
Applications in Biotechnology and Medical Research
DNA and RNA play crucial roles in biotechnology and medical research:
- Genetic Engineering:DNA manipulation techniques allow scientists to modify genes, create genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and develop new treatments for genetic diseases.
- Diagnostics:DNA and RNA analysis are used in diagnostic tests, such as genetic testing for inherited disorders or pathogen detection for infectious diseases.
- RNA Interference (RNAi):RNA molecules can be designed to silence specific genes, offering therapeutic potential for various diseases, including cancer and viral infections.
Questions Often Asked
What are the key structural differences between DNA and RNA?
DNA is a double-stranded molecule composed of deoxyribose sugar and nitrogenous bases, while RNA is a single-stranded molecule composed of ribose sugar and nitrogenous bases.
How do DNA and RNA differ in their biological roles?
DNA serves as the genetic blueprint of an organism, storing genetic information, while RNA plays a crucial role in protein synthesis, carrying genetic information from DNA to ribosomes.
How do Amoeba Sisters’ videos effectively convey the differences between DNA and RNA?
Amoeba Sisters’ videos utilize engaging animations, clear explanations, and real-world examples to illustrate the structural and functional differences between DNA and RNA, making them accessible to a wide audience.